我们解析的源码是 React18.1.0 版本,请注意版本号。React 源码学习的 GitHub 仓库地址:https://github.com/wenzi0github/react。 fiber 节点上可能会存在一些在本次调度时需要执行的任务,而且还可能存在上次调度时,优先级不够挪到当前调度的任务。 这些操作全都是函数 processUpdateQueue() 完成的,源码的位置:packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactUpdateQueue.old.js。我们在之前的 React18 源码解析之 beginWork 的操作 中稍微涉及到了点 processUpdateQueue() 的内容,但并没有展开讲解,这里我们详细说明下。 我们在讲解任务的执行之前,先明确几个属性的含义,方便我们理解。 这是 HostFiber 中 updateQueue 的基本结构: 主要涉及到两个链表: updateQueue 链表中的每个节点,都是一个 update 结构: 接下来是一些对该链表的操作。 该方法就是初始化 fiber 中的 updateQueue 结构,将 fiber 中的初始值 执行该方法 函数 为什么要做成环形链表? 在插入节点维护一个环形链表时,上操作可能比较绕,需要多理解理解。 这是一个相对来说比较复杂的操作,要考虑任务的优先级和状态的存储。 我们再总结梳理下函数 processUpdateQueue() 里的操作: 我们在上一篇文章 React18 源码解析之 beginWork 的操作 中,树的根节点是 HostRoot 类型,会调用 初始时,workInProgress.updateQueue.shared.pending 中只有一个 update 节点,这个节点中存放着一个 element 结构。 所有的 update 都执行完毕后,会再执行一条: 执行 函数 getStateFromUpdate(),可以调用 update 节点中的 payload ,对上一状态 prevState 进行处理。 根据 我们主要学习了 fiber 节点中关于链表任务的调度和执行,后续涉及到 hooks 时,也会有类似的操作。
1. 几个属性的含义 #
1.1 updateQueue 的结构 #
export type UpdateQueue<State> = {|
baseState: State, // 本次更新前该Fiber节点的state,此后的计算是基于该state计算更新后的state
firstBaseUpdate: Update<State> | null, // 上次渲染时遗留下来的低优先级任务会组成一个链表,该字段指向到该链表的头节点
lastBaseUpdate: Update<State> | null, // 该字段指向到该链表的尾节点
shared: SharedQueue<State>, // 本次渲染时要执行的任务,会存放在shared.pending中,这里是环形链表,更新时,会将其拆开,链接到 lastBaseUpdate 的后面
effects: Array<Update<State>> | null, // 存放 update.callback 不为null的update
|};
1.2 update 结构 #
const update: Update<*> = {
eventTime, // 当前操作的时间
lane, // 优先级
tag: UpdateState, // 执行的操作
/**
* 对上一个状态prevState进行操作,
* 1. 若payload是函数,则执行它:partialState = payload(prevState);否则 partialState = payload;
* 2. 若 partialState 为null,则直接返回;
* 3. partialState 与 prevState 进行合并:assign({}, prevState, partialState);
*/
payload: null,
callback: null,
next: null, // next指针
};
2. 初始化链表 initializeUpdateQueue #
fiber.memoizedState给到这个链表的 baseState 中:/**
* 初始化一个UpdateQueue,并将 updateQueue 给了 fiber
* updateQueue队列是fiber更新时要执行的内容
* @param fiber
*/
export function initializeUpdateQueue<State>(fiber: Fiber): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = {
baseState: fiber.memoizedState, // 前一次更新计算得出的状态,比如:创建时是声明的初始值 state,更新时是最后得到的 state(除去因优先级不够导致被忽略的 Update)
firstBaseUpdate: null, // 更新阶段中由于优先级不够导致被忽略的第一个 Update 对象
lastBaseUpdate: null, // 更新阶段中由于优先级不够导致被忽略的最后一个 Update 对象
shared: {
pending: null, // 更新操作的循环链表,所有的更新操作都暂时放到这里
interleaved: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
},
effects: null,
};
fiber.updateQueue = queue;
}
initializeUpdateQueue(fiber) 后,fiber 节点上就有了 updateQueue 属性了。3. 添加 update 操作 #
enqueueUpdate(update) 就是用来向链表 fiber.updateQueue.shared.pending 中添加 update 节点的。这个链表是一个循环链表,而且指针指向到该链表的最后一个节点。
/**
* 将update节点添加到fiber的updateQueue.shared.pending中
* @param fiber
* @param update
* @param lane
*/
export function enqueueUpdate<State>(fiber: Fiber, update: Update<State>, lane: Lane) {
const updateQueue = fiber.updateQueue;
if (updateQueue === null) {
// 只有在fiber已经被卸载了才会出现
// Only occurs if the fiber has been unmounted.
return;
}
const sharedQueue: SharedQueue<State> = (updateQueue: any).shared;
if (isInterleavedUpdate(fiber, lane)) {
// 省略
} else {
const pending = sharedQueue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
/**
* 当pending为null时,说明链表中还没有节点,update为第1个节点,
* 自己指向自己,最后面的pending指向到update
*/
update.next = update;
} else {
/**
* 当已经存在节点时,pending指向的是最后一个节点,pending.next是指向的第一个节点,
* update.next = pending.next:即update的next指向到了第一个节点,
* pending.next = update:即最后一个节点pending的next指针指向到了update节点,
* 这样update就进入到链表中了,此时update是链表的最后一个节点了,
* 然后下面的 sharedQueue.pending 再指向到租后一个 update 节点
*/
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
sharedQueue.pending = update;
}
}
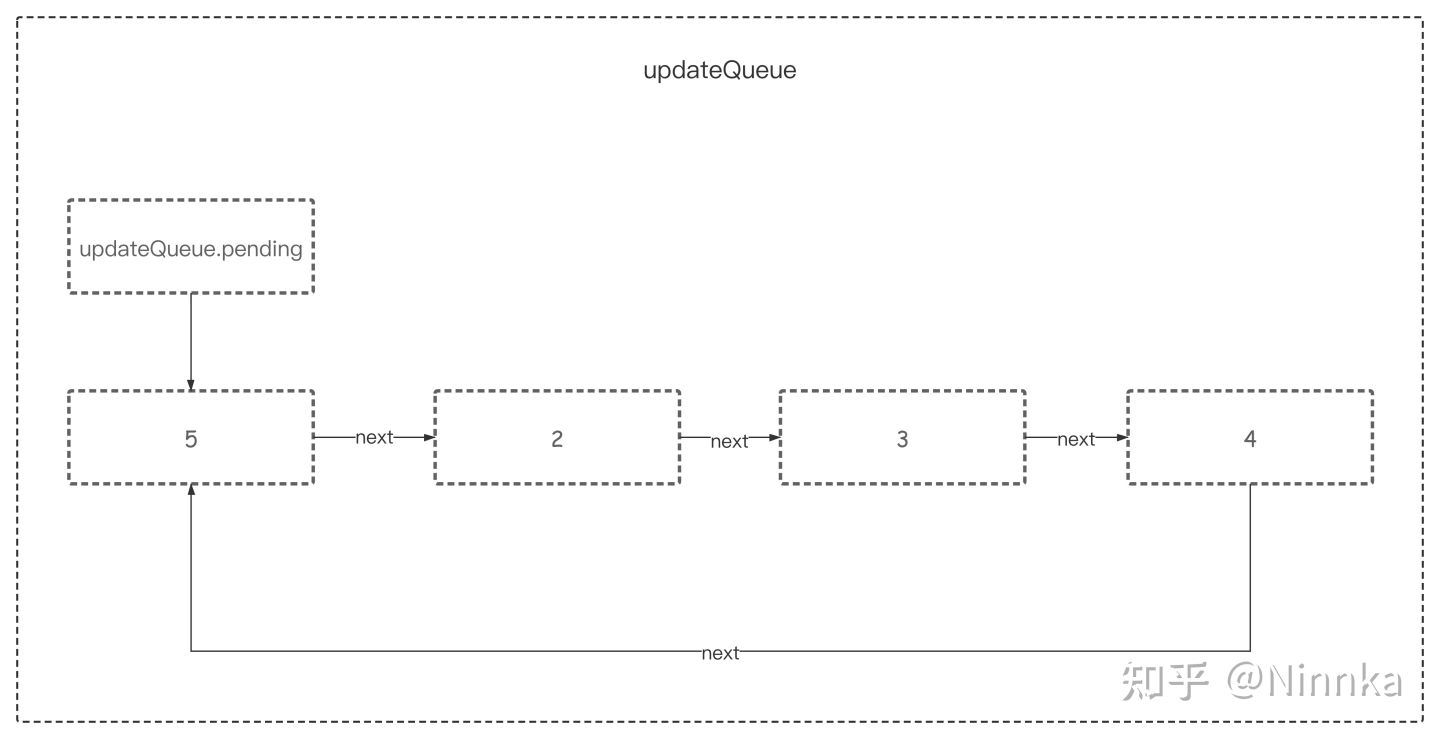
4. processUpdateQueue #
export function processUpdateQueue<State>(workInProgress: Fiber, props: any, instance: any, renderLanes: Lanes): void {
// This is always non-null on a ClassComponent or HostRoot
// 在 HostRoot和 ClassComponent的fiber节点中,updateQueue不可能为null
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = (workInProgress.updateQueue: any);
hasForceUpdate = false;
/**
* queue.shared.pending本身是一个环形链表,即使有一个节点,也会形成环形链表,
* 而且 queue.shared.pending 指向的是环形链表的最后一个节点,这里将其断开形成单向链表
* 单向链表的头指针存放到 firstBaseUpdate 中,最后一个节点则存放到 lastBaseUpdate 中
*/
let firstBaseUpdate = queue.firstBaseUpdate; // 更新链表的开始节点
let lastBaseUpdate = queue.lastBaseUpdate; // 更新链表的最后的那个节点
// 检测是否存在将要进行的更新,若存在,则将其拼接到 lastBaseUpdate 的后面,并清空刚才的链表
let pendingQueue = queue.shared.pending;
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
queue.shared.pending = null;
/**
* 若pending queue 是一个环形链表,则将第一个和最后一个节点断开,
* 环形链表默认指向的是最后一个节点,因此 pendingQueue 指向的就是最后一个节点,
* pendingQueue.next(lastPendingUpdate.next)就是第一个节点了
*/
const lastPendingUpdate = pendingQueue; // 环形链表的最后一个节点
const firstPendingUpdate = lastPendingUpdate.next; // 环形链表的第一个节点
lastPendingUpdate.next = null; // 最后一个节点与第一个节点断开
/**
* 将 pendingQueue 拼接到 更新链表 queue.firstBaseUpdate 的后面
* 1. 更新链表的最后那个节点为空,说明当前更新链表为空,把要更新的首节点 firstPendingUpdate 给到 firstBaseUpdate即可;
* 2. 若更新链表的尾节点不为空,则将要更新的首节点 firstPendingUpdate 拼接到 lastBaseUpdate 的后面;
* 3. 拼接完毕后,lastBaseUpdate 指向到新的更新链表最后的那个节点;
*/
// Append pending updates to base queue
if (lastBaseUpdate === null) {
firstBaseUpdate = firstPendingUpdate;
} else {
lastBaseUpdate.next = firstPendingUpdate;
}
lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
/**
* 若workInProgress对应的在current的那个fiber节点,其更新队列的最后那个节点与当前的最后那个节点不一样,
* 则我们将上面「将要更新」的链表的头指针和尾指针给到current节点的更新队列中,
* 拼接方式与上面的一样
*/
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
// This is always non-null on a ClassComponent or HostRoot
const currentQueue: UpdateQueue<State> = (current.updateQueue: any);
const currentLastBaseUpdate = currentQueue.lastBaseUpdate;
// 若current更新链表的最后那个节点与当前将要更新的链表的最后那个节点不一样
// 则,把将要更新的链表也拼接到current中
if (currentLastBaseUpdate !== lastBaseUpdate) {
if (currentLastBaseUpdate === null) {
currentQueue.firstBaseUpdate = firstPendingUpdate;
} else {
currentLastBaseUpdate.next = firstPendingUpdate;
}
currentQueue.lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
}
}
}
/**
* 进行到这里,render()初始更新时,放在 queue.shared.pending 中的update节点(里面存放着element结构),
* 就已经放到 queue.firstBaseUpdate 里了,
* 因此 firstBaseUpdate 里肯定存放了一个 update 节点,一定不为空,进入到 if 的逻辑中
*/
// These values may change as we process the queue.
if (firstBaseUpdate !== null) {
// Iterate through the list of updates to compute the result.
// 迭代更新列表以计算结果
/**
* newState 先拿到上次的数据,然后执行 firstBaseUpdate 链表中所有的 update,
* 再存储每轮的结果,最后将其给到 workInProgress.memoizedState
* 默认值:
* {
* cache: {controller: AbortController, data: Map(0), refCount: 1}
* element: null
* isDehydrated: false
* pendingSuspenseBoundaries: null
* transitions: null
* }
*/
let newState = queue.baseState;
// TODO: Don't need to accumulate this. Instead, we can remove renderLanes
// from the original lanes.
let newLanes = NoLanes;
/**
* 下次渲染时的初始值
* 1. 若存在低优先级的任务,则该 newBaseState 为第一个低优先级任务之前计算后的值;
* 2. 若不存在低优先级的任务,则 newBaseState 为执行完所有任务后得到的值;
*/
let newBaseState = null;
/**
* 下面的两个指针用来存放低优先级的更新链表,
* 即 firstBaseUpdate 链表中,可能会存在一些优先级不够的update,
* 若存在低优先级的update,则将其拼接到 newFirstBaseUpdate 里,
* 同时,既然存在低优先级的任务,为了保证整个更新的完整性,也会将已经执行update后的结果,也放到这个新链表中,
* 这里存在一个问题,若低优先级任务是中间才出现的,怎么办呢?
* 解决方案:将执行到当前update前的state设置为新链表的初始值:newBaseState = newState;
*/
let newFirstBaseUpdate = null; // 新的更新链表的头指针
let newLastBaseUpdate = null; // 新的更新链表的尾指针
let update = firstBaseUpdate; // 从第1个节点开始执行
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
const updateEventTime = update.eventTime;
/**
* 判断 updateLane 是否是 renderLanes 的子集,
* if 这里有个取反的符号,导致理解起来可能有点困难,实际上:
* 1. 若 update 的 lane (又名 updateLane) 是 renderLanes 的子集,则执行该update;
* 2. 若不是其子集,则将其放到心的队列中,等待下次的执行;
*/
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {
// Priority is insufficient. Skip this update. If this is the first
// skipped update, the previous update/state is the new base
// update/state.
/**
* 若当前 update 的操作的优先级不够。跳过此更新。
* 将该update放到新的队列中,为了保证链式操作的连续性,下面else逻辑中已经可以执行的update,也放到这个队列中,
* 这里还有一个问题,从第一个低优先级的任务到最后都已经存储起来了,那新的初始状态是什么呢?
* 新的初始状态就是当前跳过的update节点时的那个状态。新的初始状态,只有在第一个跳过任务时才需要设置。
* 例如我们初始状态是0,有10个update的操作,第0个update的操作是+0,第1个update的操作是+1,第2个update的操作是+2,依次类推;
* 若第4个update是一个低优先级的操作,其他的都是正常的优先级。
* 那么将第4个update放到新的链表进行存储时,此时要存储的初始值就是执行当前节点前的值,是6(state+0+1+2+3)
* 后续的update即使当前已经执行过了,也是要放到新的链表中的,否则更新就会乱掉。
* 下次渲染时,就是以初始state为6,+4的那个update开始,重新判断优先级
*/
const clone: Update<State> = {
eventTime: updateEventTime,
lane: updateLane,
tag: update.tag,
payload: update.payload,
callback: update.callback,
next: null,
};
// 拼接低优先级的任务
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) {
// 还没有节点,这clone就是头结点
// 并将此时的 newState 放到新的 newBaseState中
newFirstBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate = clone;
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
// 已经有节点了,直接向后拼接
newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;
}
// Update the remaining priority in the queue.
newLanes = mergeLanes(newLanes, updateLane);
} else {
// This update does have sufficient priority.
// 此更新具有足够的优先级
// 初始render()时会走这里
if (newLastBaseUpdate !== null) {
/**
* 若存储低优先级的更新链表不为空,则为了操作的完整性,即使当前update会执行,
* 也将当前的update节点也拼接到后面,
* 但初始render()渲染时,newLastBaseUpdate为空,走不到 if 这里
*/
const clone: Update<State> = {
eventTime: updateEventTime,
// This update is going to be committed so we never want uncommit
// it. Using NoLane works because 0 is a subset of all bitmasks, so
// this will never be skipped by the check above.
/**
* 翻译:这次update将要被提交更新,因此后续我们不希望取消这个提交。
* 使用 NoLane 这个是可行的,因为0是任何掩码的子集,
* 所以上面 if 的检测`isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)`,永远都会为真,
* 该update永远不会被作为低优先级进行跳过,每次都会执行
*/
lane: NoLane,
tag: update.tag,
payload: update.payload,
callback: update.callback,
next: null,
};
// 拼接到低优先级链表的后面
newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;
}
// Process this update.
/**
* render()时 newState 的默认值:
* {
* cache: {controller: AbortController, data: Map(0), refCount: 1}
* element: null
* isDehydrated: false
* pendingSuspenseBoundaries: null
* transitions: null
* }
* 执行 getStateFromUpdate() 后,则会将 update 中的 element 给到 newState 中
*/
newState = getStateFromUpdate(workInProgress, queue, update, newState, props, instance);
const callback = update.callback;
if (
callback !== null &&
// If the update was already committed, we should not queue its
// callback again.
update.lane !== NoLane
) {
workInProgress.flags |= Callback;
const effects = queue.effects;
if (effects === null) {
queue.effects = [update];
} else {
effects.push(update);
}
}
}
update = update.next; // 初始render()时,只有一个update节点,next为null,直接break,跳出循环
if (update === null) {
/**
* 在上面将 queue.shared.pending 放到firstBaseUpdate时,
* queue.shared.pending就已经重置为null了
* @type {Update
*/
pendingQueue = queue.shared.pending;
if (pendingQueue === null) {
break;
} else {
// An update was scheduled from inside a reducer. Add the new
// pending updates to the end of the list and keep processing.
/**
* 猜的,在优先级调度过程中,又有了新的更新到来,则此时再拼接到更新队列的后面,接着循环处理
*/
const lastPendingUpdate = pendingQueue;
// Intentionally unsound. Pending updates form a circular list, but we
// unravel them when transferring them to the base queue.
const firstPendingUpdate = ((lastPendingUpdate.next: any): Update<State>);
lastPendingUpdate.next = null;
update = firstPendingUpdate;
queue.lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
queue.shared.pending = null;
}
}
} while (true);
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) {
// 若没有任意的低优先级的任务呢,则将一串的update执行后的结果,就是新的 baseState,
// 若有低优先级的任务,则已经在上面设置过 newBaseState 了,就不能在这里设置了
newBaseState = newState;
}
queue.baseState = ((newBaseState: any): State); // 下次更新时,要使用的初始值
queue.firstBaseUpdate = newFirstBaseUpdate;
queue.lastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate;
/**
* 经过上面的操作,queue(即 workInProgress.updateQueue )为:
* baseState: { element: element结构, isDehydrated: false }
* effects: null,
* firstBaseUpdate: null,
* lastBaseUpdate: null,
* shared: { pending: null, interleaved: null, lanes: 0 }
*/
// workInProgress.updateQueue的数据结构: https://mat1.gtimg.com/qqcdn/tupload/1659687672451.png
// Interleaved updates are stored on a separate queue. We aren't going to
// process them during this render, but we do need to track which lanes
// are remaining.
const lastInterleaved = queue.shared.interleaved;
if (lastInterleaved !== null) {
let interleaved = lastInterleaved;
do {
newLanes = mergeLanes(newLanes, interleaved.lane);
interleaved = ((interleaved: any).next: Update<State>);
} while (interleaved !== lastInterleaved);
} else if (firstBaseUpdate === null) {
// `queue.lanes` is used for entangling transitions. We can set it back to
// zero once the queue is empty.
queue.shared.lanes = NoLanes;
}
// Set the remaining expiration time to be whatever is remaining in the queue.
// This should be fine because the only two other things that contribute to
// expiration time are props and context. We're already in the middle of the
// begin phase by the time we start processing the queue, so we've already
// dealt with the props. Context in components that specify
// shouldComponentUpdate is tricky; but we'll have to account for
// that regardless.
markSkippedUpdateLanes(newLanes);
workInProgress.lanes = newLanes;
workInProgress.memoizedState = newState; // 存储本次最新的结果
}
}
processUpdateQueue() 函数。我们在了解其内部的调度后,就更加清晰了。
DefaultLane,即不会跳过任何一个任务;workInProgress.memoizedState = newState;
// workInProgress.memoizedState = { element };
processUpdateQueue() 完毕后,workInProgress 节点的 memoizedState 属性上,就已经挂载 element 结构了。5. 对上一个状态 prevState 进行操作 #
update.tag 也是区分了几种情况:
function getStateFromUpdate<State>(
workInProgress: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<State>,
update: Update<State>,
prevState: State,
nextProps: any,
instance: any,
): any {
/**
* 可以看到下面也是区分了几种情况
* 1. ReplaceState:舍弃掉旧状态,直接用新状态替换到旧状态;
* 2. UpdateState:新状态和旧状态的数据合并后再返回;
* 3. ForceUpdate:只修改 hasForceUpdate 为true,不过返回的还是旧状态;
*/
switch (update.tag) {
case ReplaceState: {
const payload = update.payload;
if (typeof payload === 'function') {
// Updater function
// 若payload是function,则将prevState作为参数传入,执行payload()
// 直接返回该函数执行后的结果(不再与之前的数据进行合并)
const nextState = payload.call(instance, prevState, nextProps);
return nextState;
}
// 若不是function类型,则传入什么,返回什么
// State object
return payload;
}
case CaptureUpdate: {
workInProgress.flags = (workInProgress.flags & ~ShouldCapture) | DidCapture;
}
// Intentional fallthrough
case UpdateState: {
const payload = update.payload;
let partialState; // 用于存储计算后的新state结果,方便最后进行assign合并处理
if (typeof payload === 'function') {
// Updater function
// 若payload是function,则将prevState作为参数传入,执行payload()
partialState = payload.call(instance, prevState, nextProps);
} else {
// Partial state object
// 若 payload 是变量,则直接赋值
partialState = payload;
}
if (partialState === null || partialState === undefined) {
// Null and undefined are treated as no-ops.
// 若得到的结果是null或undefined,则返回之前的数据
return prevState;
}
// Merge the partial state and the previous state.
// 与之前的state数据进行合并
return assign({}, prevState, partialState);
}
case ForceUpdate: {
hasForceUpdate = true;
return prevState;
}
}
return prevState;
}
update.payload的类型不一样,执行的操作也不一样:
6. 总结 #
版权属于:
加速器之家
作品采用:
《
署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
》许可协议授权

评论