我们解析的源码是 React18.1.0 版本,请注意版本号。React 源码学习的 GitHub 仓库地址:https://github.com/wenzi0github/react。 我们接下来的文章是进行 React 源码解析的,已默认您已很熟练使用 React,并阅读过React 的官方文档。 我们在阅读 React 源码之前,先熟悉几个概念,这样读起来会顺畅很多。 我们在 React 中写的类似于 html 的结构就被称为 JSX,但他并不是 html,而是一个 JavaScript 的语法扩展。即他是 js,而不是 html。 官方文档: 这里我们不讲解 jsx 的使用方式,主要说下 JSX 的作用。jsx 是 js 的语法糖,方便我们开发者的维护。最后实际上会被 React(React16.x 及之前)或 babel 编译(React17.0 及更新)成用 createElement 编译的结构。 同样的,我们在 React 中像下面这样写的效果是一样的: 但这种方式使用起来确实不方便。 上面提到会将 jsx 编译成由 createElement()函数组成的一个嵌套结果。那么 createElement 里具体都干了什么呢? 在 React16 及之前,createElement()方法是 React 中的一个方法,因此有些同学就会有疑问,在写 最终转换出的代码是: 但从 React17 开始,React 和 babel 合作,将 jsx 的转换工作放到了编译工具 babel 中。新的 JSX 转换不会将 JSX 转换为 React.createElement,而是自动从 React 的 package 中引入新的入口函数并调用。 假设你的源代码如下: 下方是新 JSX 被转换编译后的结果: 注意,此时源代码无需引入 React 即可使用 JSX 了!若仍然要使用 React 提供的 Hook 等功能,还是需要引入 React 的。 可以看到新 jsx()和之前的 React.createElement()方法转换出来的结构稍微有点区别。之前的 React.createElement()方法里,子结构会通过第三个参数进行传入;而在 jsx()方法中,这里将子结构放到了第二个参数的 children 字段里,第 3 个字段则用于传入设置的 key 属性。若子结构中只有一个子元素,那么 children 就是一个 jsx(),若有多个元素时,则会转为数组: 这里有个 babel 的在线网站,我们可以编写一段 React 代码,能实时看到通过 babel 编译后的效果:React 通过 babel 实现新的 jsx 转换。若 jsx 的转换方式还是旧版的,请在左侧的配置中,将 React Runtime 设置为 automatic 。 那么 jsx()方法里具体是怎么执行的呢?最后返回了样子的数据呢?源码位置:jsx()。 jsx()方法会先进行一系列的判断,相关链接: 介绍全新的 JSX 转换。jsx()方法中,会经过一些判断,将 key 和 ref 两个比较特殊的属性单独提取出来。 ReactElement()方法的作用就是返回一个 object 结构,我们这里把所有的提示代码都去掉: 上面方法注释的大概意思是:现在不再使用类的方式 new 出一个实例来,因此不再使用 instanceOf 来判断是否是 React 元素;而是判断 我们已经知道 到目前位置,我们已经知道了 jsx 在传入 render()方法之前,会编译成什么样子。 我们在 在控制台里就能看到这样的结构: 我们再输出一个完整的组件,如一个 App 组件如下: 分别输出下 App 和 单纯的 我们在上面的代码中已经说了 type 字段的含义,这里再说下跟 type 相关的 children 字段。当 type 为 html 标签时,children 就其下面所有的子节点。当只有一个子节点时,children 为 object 类型,当有多个子节点时,children 是 array 类型。 有些同学可能一时反应不过来,觉得组件 这里 因此,在传入到 render()方法时,就是这样子的一个 object 类型的 element 元素。 在上面通过 babel 转换后的 object 类似的数据,会在 render()方法中将其转为 fiber 结构。render()方法里具体怎样转换的,我们稍后再讲,这里我们只是看下 fiber 节点的结构。 React 中大到组件,小到 html 标签,都会转为 fiber 节点构建的 fiber 链表。 为什么要使用 fiber 链表?这里我们稍微了解下,后面会详细介绍 fiber 链表如何进行 diff 每个 fiber 节点的。 在 React 15.x 版本以及之前的版本,Reconciliation 算法采用了栈调和器( Stack Reconciler )来实现,但是这个时期的栈调和器存在一些缺陷:不能暂停渲染任务,不能切分任务,无法有效平衡组件更新渲染与动画相关任务的执行顺序,即不能划分任务的优先级(这样有可能导致重要任务卡顿、动画掉帧等问题)。Stack Reconciler 的实现。 为了解决 Stack Reconciler 中固有的问题,以及一些历史遗留问题,在 React 16 版本推出了新的 Reconciliation 算法的调和器—— Fiber 调和器(Fiber Reconciler)来替代栈调和器。Fiber Reconciler 将会利用调度器(Scheduler)来帮忙处理组件渲染/更新的工作。此外,引入 fiber 这个概念后,原来的 react element tree 有了一棵对应的 fiber node tree。在 diff 两棵 react element tree 的差异时,Fiber Reconciler 会基于 fiber node tree 来使用 diff 算法,通过 fiber node 的 return、child、sibling 属性能更方便的遍历 fiber node tree,从而更高效地完成 diff 算法。 fiber 调度的优点: fiber 现在是整个 React 应用的基础,无论是整个结构树,还是优先级的调度,或者是 diff 对比等,都是以 fiber 为基础的。1. 什么是 jsx #
const App = () => {
const handleClick = () => {
console.log('click');
};
return (
<div onClick={handleClick}>
<p>hello worldp>
div>
);
};
createElement('div', { onClick: handleClick }, createElement('p', null, 'hello world'));
2. createElement 是用来干嘛的 #
.jsx的组件时,本来没用到 React 中的方法,但还是要引入 React。就如上面的代码,在 React16 及之前,要在头部显式地将 React 引入进来的。import React from 'react';
React.createElement('div', { onClick: handleClick }, React.createElement('p', null, 'hello world'));
function App() {
return <h1>Hello Worldh1>;
}
// 由编译器引入(禁止自己引入!)
import { jsx as _jsx } from 'react/jsx-runtime';
function App() {
return _jsx('h1', { children: 'Hello world' });
}
const App = () => {
return jsx('div', {
children: jsx('p', {
children: [
jsx('span', {
className: 'dd',
children: 'hello world',
}),
_jsx('span', {
children: '123',
}),
],
}),
});
};
/**
* 将jsx编译为普通的js树形结构
* @param {string|function} type 若节点为普通html标签时,type为标签的tagName,若为组件时,即为该函数
* @param {object} config 该节点所有的属性,包括children
* @param {string?} maybeKey 显式地设置的key属性
* @returns {*}
*/
export function jsx(type, config, maybeKey) {
let propName;
// Reserved names are extracted
const props = {};
let key = null;
let ref = null;
// 若设置了key,则使用该key
if (maybeKey !== undefined) {
if (__DEV__) {
checkKeyStringCoercion(maybeKey);
}
key = '' + maybeKey;
}
// 若config中设置了key,则使用config中的key
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
if (__DEV__) {
checkKeyStringCoercion(config.key);
}
key = '' + config.key;
}
// 提取设置的ref属性
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref;
}
// Remaining properties are added to a new props object
// 剩余属性将添加到新的props对象中
for (propName in config) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) && !RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
/**
* 我们的节点有有三种类型:
* 1. 普通的html标签,type为该标签的tagName,如div, span等;
* 2. 当前是Function Component节点时,则type该组件的函数体,即可以执行type();
* 3. 当前是Class Component节点,则type为该class,可以new出一个实例;
* 而type对应的是Function Component时,可以给该组件添加defaultProps属性,
* 当设置了defaultProps,则将未明确传入的属性给到props里
*/
// Resolve default props
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
const defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
/**
* 参数处理完成后,就调用ReactElement()方法返回一个object结构
*/
return ReactElement(type, key, ref, undefined, undefined, ReactCurrentOwner.current, props);
}
/**
* Factory method to create a new React element. This no longer adheres to
* the class pattern, so do not use new to call it. Also, instanceof check
* will not work. Instead test $$typeof field against Symbol.for('react.element') to check
* if something is a React Element.
*/
const ReactElement = function(type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
const element = {
// This tag allows us to uniquely identify this as a React Element
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE, // 用来标识当前是否是React元素
/**
* 我们的节点有有三种类型:
* 1. 普通的html标签,type为该标签的tagName,如div, span等;
* 2. 当前是Function Component节点时,则type该组件的函数体,即可以执行type();
* 3. 当前是Class Component节点,则type为该class,可以通过该type,new出一个实例;
* 而type对应的是Function Component时,可以给该组件添加defaultProps属性,
* 当设置了defaultProps,则将未明确传入的属性给到props里
*/
// Built-in properties that belong on the element
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner,
};
return element;
};
$$typeof 字段是否等于Symbol.for('react.element')来判断。$$typeof 字段的作用是为了标识 React 元素的,但他的值为什么用 Symbol 类型呢?可以参考这篇文章:为什么React元素有一个$$typeof属性?*.jsx文件中,先直接输出下 jsx 的结构:console.log(
<div>
<span>hello worldspan>
div>,
);
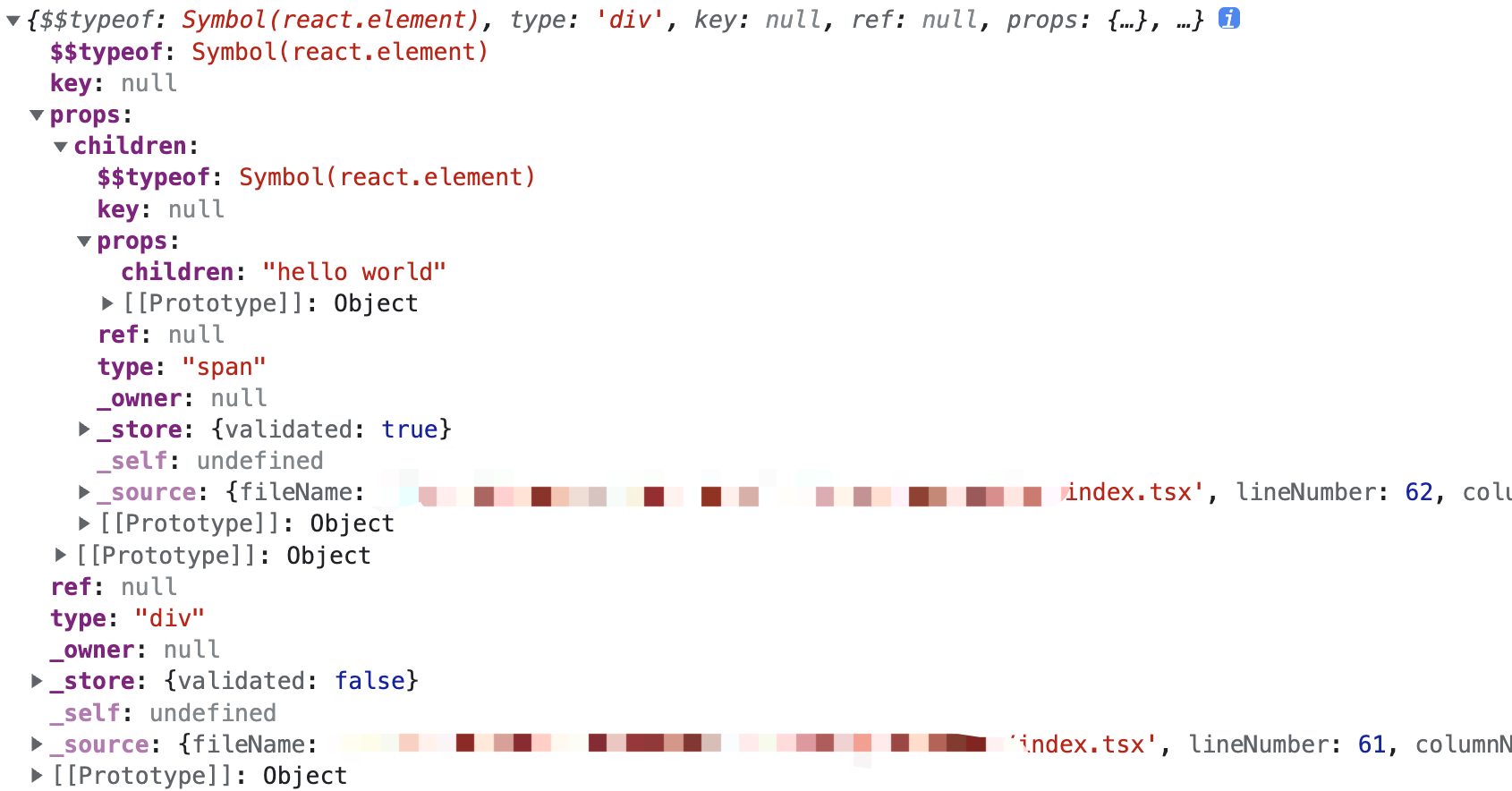
const element = {
$$typeof: Symbol(react.element),
key: null,
props: {
children: {
// 当children有多个时,会转为数组类型
$$typeof: Symbol(react.element),
key: null,
props: {
children: 'hello world', // 文本节点没有类型
},
ref: null,
type: 'span',
},
},
ref: null,
type: 'div',
};
const App = ({ username }) => {
return (
<div>
<span>hello {username}span>
div>
);
};
console.log(<App />, App);
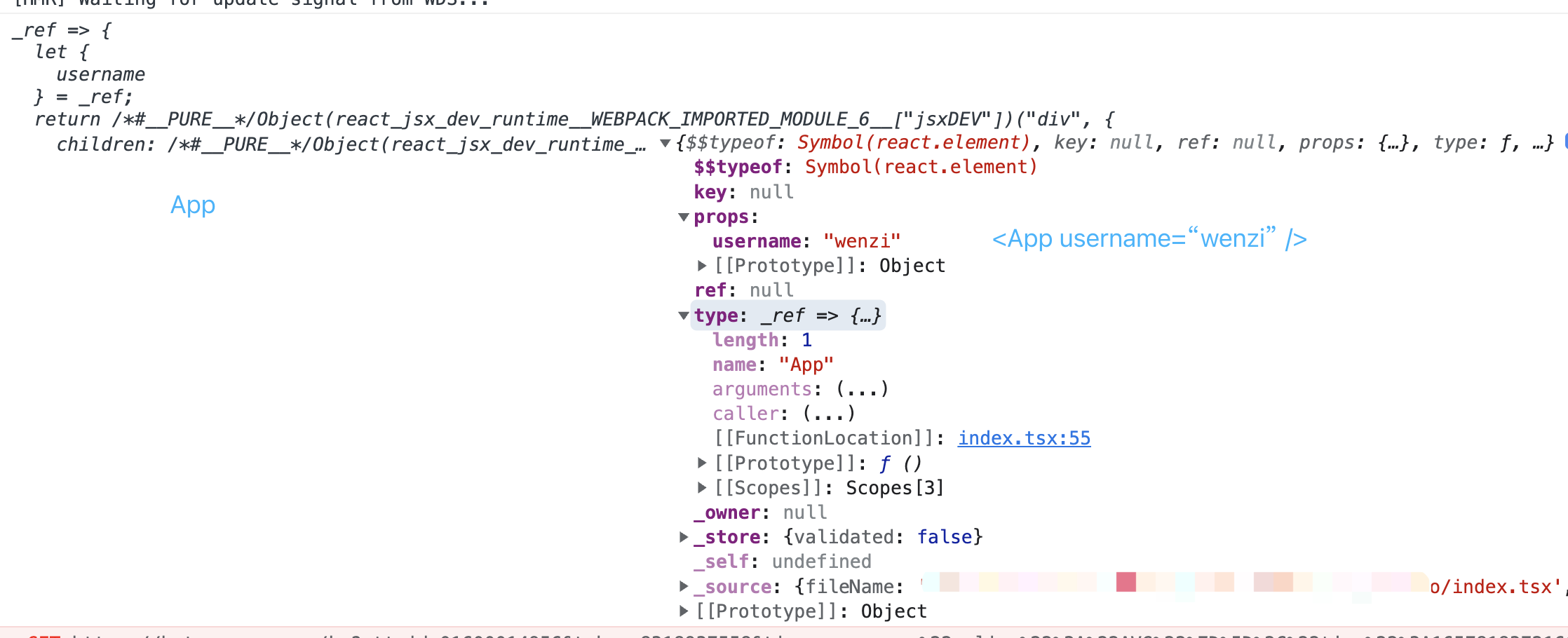
App是一个函数,function 类型,但这里不能直接执行App(),会报错的;而type字段对应的 function 或 class 来获得。如:const Start = (
<div>
<App>
<p>this is app childrenp>
App>
div>
);
3. fiber 结构 #
/**
* 创建fiber节点
* @param {WorkTag} tag
* @param {mixed} pendingProps
* @param {null | string} key
* @param {TypeOfMode} mode
* @constructor
*/
function FiberNode(tag: WorkTag, pendingProps: mixed, key: null | string, mode: TypeOfMode) {
// Instance
this.tag = tag; // 当前节点的类型,如 FunctionComponent, ClassComponent 等
/**
* 这个字段和 react element 的 key 的含义和内容有一样(因为这个 key 是
* 从 react element 的key 那里直接拷贝赋值过来的),作为 children 列表
* 中每一个 item 的唯一标识。它被用于帮助 React 去计算出哪个 item 被修改了,
* 哪个 item 是新增的,哪个 item 被删除了。
* @type {string}
*/
this.key = key;
this.elementType = null;
/**
* 当前fiber节点的元素类型,与React Element里的type类型一样,若是原生的html标签,
* 则 type 为该标签的类型('div', 'span' 等);若是自定义的Class Component或
* Function Component等,则该type的值就是该class或function,后续会按照上面的tag字段,
* 来决定是用new初始化一个实例(当前是 Class Component),然后执行该class内
* 的render()方法;还是执行该type(当前是 Function Component),得到其返回值;
*/
this.type = null;
/**
* 1. 若当前fiber节点是dom元素,则对应的是真实DOM元素;
* 2. 若当前是function component,则值为null;
* 3. 若当前是class component,则值为class初始化出来的实例
*/
this.stateNode = null;
/**
* 下面的return, child和sibling都是指针,用来指向到其他的fiber节点,
* React会将jsx编译成的element结构,转为以fiber为节点的链表结构,
* return: 指向到父级fiber节点;
* child: 指向到该节点的第1个子节点;
* sibling: 指向到该节点的下一个兄弟节点;
* 如图所示:https://pic4.zhimg.com/80/v2-a825372d761879bd1639016e6db93947_1440w.jpg
*/
this.return = null;
this.child = null;
this.sibling = null;
this.index = 0;
this.ref = null;
this.pendingProps = pendingProps;
this.memoizedProps = null;
this.updateQueue = null;
this.memoizedState = null;
this.dependencies = null;
this.mode = mode;
// Effects
this.flags = NoFlags; // 该节点更新的优先级,若为NoFlags时,则表示不更新
this.subtreeFlags = NoFlags; // 子节点的更新情况,若为NoFlags,则表示其子节点不更新,在diff时可以直接跳过
this.deletions = null; // 子节点中需要删除的节点
this.lanes = NoLanes;
this.childLanes = NoLanes;
/**
* 双缓冲:防止数据丢失,提高效率(之后Dom-diff的时候可以直接比较或者使用
* React在进行diff更新时,会维护两颗fiber树,一个是当前正在展示的,一个是
* 通过diff对比后要更新的树,这两棵树中的每个fiber节点通过 alternate 属性
* 进行互相指向。
*/
this.alternate = null;
}
3.1 Stack Reconciler #
3.2 Fiber Reconciler #
4. 总结 #
版权属于:
加速器之家
作品采用:
《
署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
》许可协议授权

评论